मानचित्रण का इतिहास
मानचित्रण का इतिहास: मेरी रचनाओं में से एक गीत – रेत में मौसम की लिखावट, टेढ़े-मेढ़े पत्थर पर माप, या गीतों और कला में डरा हुआ भूगोल – सभी संस्कृतियों में आम है। सबसे पुराने जीवित मानचित्र और चार्ट प्राचीन बेबीलोनिया और मिस्र से प्राप्त होते हैं। तीसरी सहस्राब्दी ईसा पूर्व तक, दोनों के पास आवश्यक गणितीय और प्रारूपण कौशल थे, और नौकरशाही बेबीलोनियन कार्टोग्राफी के सर्वेक्षण और मानचित्रण के लिए जिम्मेदार थी, जो ज्यादातर आंशिक थी, जबकि मिस्र के मानचित्रों में पौराणिक भूमि और जीवन के बाद के मार्गों का मानचित्रण किया गया था।
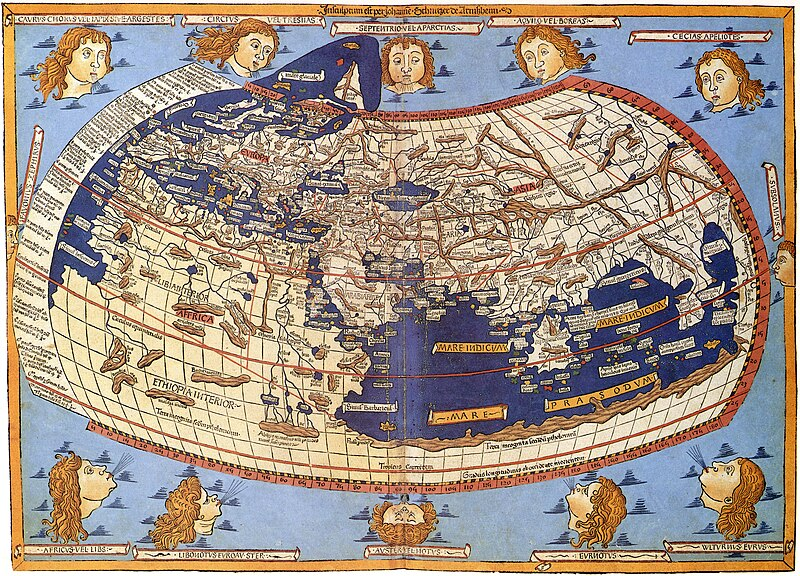
मानचित्रण का इतिहास:: यूनानियों ने पृथ्वी और ब्रह्मांड की प्रकृति की जांच करते हुए पश्चिमी मानचित्रकला की वैज्ञानिक नींव रखी। रोमनों ने अधिकतर संपत्तियों, नगर योजनाओं और सड़कों का मानचित्रण किया। साथ ही, चीनियों ने अपने मानचित्रों में कला और मौखिक कथा को शामिल किया, फिर भी वे सैन्य योजना और राज्य सुरक्षा को लेकर भी चिंतित थे। जापान और कोरिया भी अपने विश्व मानचित्रों के लिए चीन पर निर्भर थे और उन्होंने स्वयं को हाशिये पर डाल लिया।
मानचित्रण का इतिहास: मध्य युग में धार्मिक मानचित्रकला का बोलबाला था। हालाँकि अरबों ने शास्त्रीय बौद्धिक परंपरा को बनाए रखा और अपनी इस्लामी मानचित्र-निर्माण परंपरा भी विकसित की।
मानचित्रण का इतिहास: प्रिंटिंग प्रेस के आविष्कार और भूगोल के लिए टॉलेमी की मार्गदर्शिका की पुनः खोज ने पश्चिमी यूरोप में वैज्ञानिक मानचित्रकला में पुनरुद्धार को बढ़ावा दिया, जो कि स्पेनिश और पुर्तगालियों द्वारा अफ्रीका, अमेरिका और स्पाइस द्वीपों की यात्राओं से तेज हुआ। फ्रांसीसी आधिकारिक भूमि सर्वेक्षण करने वाले पहले व्यक्ति बने, जिन्होंने 1787 तक 182 मानचित्र शीट तैयार कीं। ब्रिटिशों ने 19वीं शताब्दी की शुरुआत में भारत के महान त्रिकोणमितीय सर्वेक्षण का निर्माण करने के लिए फ्रांसीसी तकनीक को अपनाया।
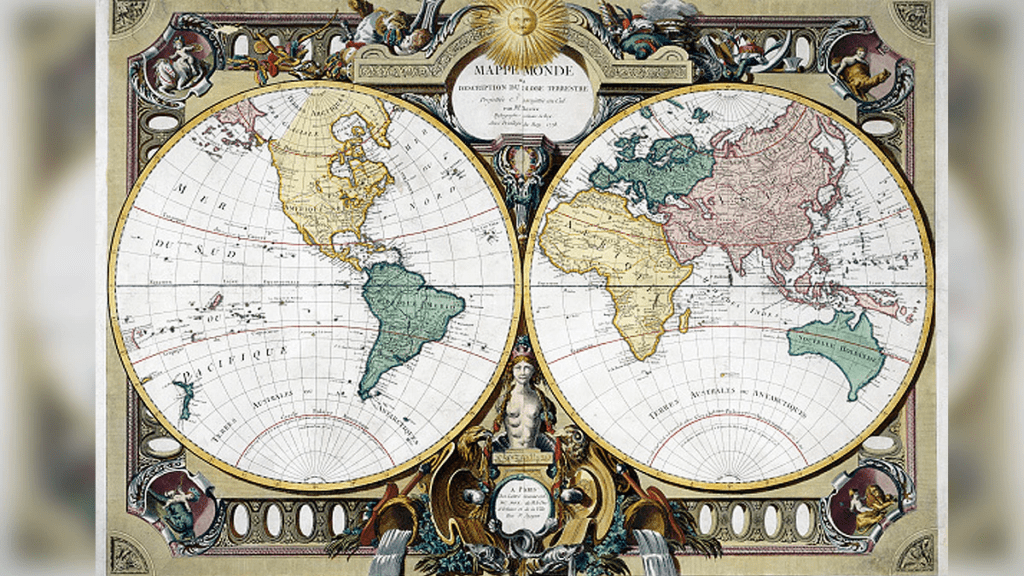
ऑर्टेलियस और मर्केटर, अग्रणी मानचित्र निर्माता
मानचित्रण का इतिहास: एक युवा फ्लेमिश विद्वान और भूगोलवेत्ता के रूप में, अब्राहम ऑर्टेलियस (1527-1588) को मानचित्र पांडुलिपियों को कुशलतापूर्वक प्रकाशित करने और पुस्तकों और सिक्कों के संग्रह के लिए जाना जाता था। एक बार कार्डियोग्राफर के रूप में स्थापित होने के बाद, उन्होंने 1570 में थियेट्रम ऑर्बिसटेरारम, या थिएटर ऑफ़ द वर्ल्ड के प्रकाशन के साथ पुनर्जागरण की दुनिया में क्रांति ला दी। इसे प्रथम मॉडल एटलस के रूप में जाना जाता है।
थिएट्रम एक बड़ी सफलता साबित हुई और उसने यूरोपीय मानचित्र व्यापार के केंद्र को रोम और वेनिस से एंटवर, उसके घर में स्थानांतरित करने में मदद की। जब वह वहां है, और आप उसका घर हैं। 31 संस्करण और 7 भाषाओं में लगभग 7,300 प्रतियां मुद्रित की गईं और आज लगभग 1,630 डॉलर के बराबर कीमत पर बेची गईं, जिससे ऑर्टेलियस बहुत अमीर हो गया।
थिएटरम में ऑर्टेलियस मित्र और साथी फ्लेमिश कार्डियोग्राफर, जेरार्डस मर्केटर, 1512-1594 द्वारा तैयार विश्व प्रक्षेपण की एक पृष्ठ की कमी शामिल है। पहली बार 1569 में प्रकाशित, मर्केटर प्रोजेक्शन को नेविगेशन जोड़ने के लिए डिज़ाइन किया गया था। अक्षांश और देशांतर में सभी रेखाओं को सीधी रेखाओं के रूप में दर्शाए जाने से, नाविक अधिक आसानी से लंबी दूरी तक अपना रास्ता बना सकते हैं।

मानचित्रण का इतिहास: अपने मूल समुद्री उद्देश्य के बावजूद, मेरेटर प्रक्षेपण, संशोधन के साथ, 20वीं शताब्दी तक दुनिया का एक मानक द्वि-आयामी प्रतिनिधित्व बन गया। स्कूली बच्चों की पीढ़ियों ने मर्केटर प्रोजेक्शन का अध्ययन किया है, जिससे उन्हें विश्वास हो गया कि ग्रीनलैंड और अफ्रीका लगभग एक ही आकार के हैं, हालांकि वे वास्तव में 14 गुना बड़े हैं।
आधुनिक मानचित्र
मानचित्रण का इतिहास: सर्वेक्षण और मानचित्रण की वैज्ञानिक विधियों का 17वीं, 18वीं और 19वीं शताब्दी में काफी विस्तार हुआ, आंशिक रूप से अधिक परिष्कृत गणितीय अनुप्रयोगों के साथ-साथ बड़े क्षेत्रों के कठोर और व्यापक सर्वेक्षणों के कारण।
आज सर्वेक्षण में अक्सर रिमोट सेंसिंग के तत्वों का उपयोग किया जाता है – दूर से किसी वस्तु या क्षेत्र के बारे में जानकारी प्राप्त करना। किसी ऊंची इमारत की चोटी से किसी शहर को या ऊंचे पहाड़ की चोटी से किसी गांव को देखना रिमोट सेंसिंग का एक रूप है। मानचित्र निर्माता समान परिणाम प्राप्त करने के लिए अधिक परिष्कृत तरीकों का उपयोग करते हैं।
एरियल फोटोग्राफी, जिसका उपयोग कुछ हद तक प्रथम विश्व युद्ध के दौरान किया गया था, द्वितीय विश्व युद्ध के दौरान मानचित्र-निर्माण में रिमोट सेंसिंग उपकरण के रूप में व्यापक हो गई। इसने सर्वेक्षकों की अधिकांश कठिनाइयों को समाप्त कर दिया और कुछ अन्य दुर्गम स्थानों को सटीक सर्वेक्षण आवंटित कर दिया।
रडार, या रेडियो तरंगों और सोनार, या ध्वनि तरंगों द्वारा रिमोट सेंसिंग, समुद्र तल पर भूमि की सतह की विशेषताओं को रिकॉर्ड करने का एक और तरीका प्रदान करता है। दोनों तरीकों में, दूरी की गणना लक्ष्य क्षेत्र तक पहुंचने में लगने वाले समय से की जाती है। दूर से संवेदित छवियां उनके द्वारा दर्शाए गए रिज़ॉल्यूशन के प्रकार के आधार पर भिन्न होती हैं।
स्थानिक रिज़ॉल्यूशन से तात्पर्य यह है कि कोई छवि कितनी तेज़ है। अधिक दूरी को आमतौर पर धुंधली छवियों के बराबर माना जाता है।
स्पेक्ट्रल रिज़ॉल्यूशन से तात्पर्य है कि प्रकाश स्पेक्ट्रम के किस हिस्से को कैप्चर किया जा रहा है और इसमें दृश्य प्रकाश या अवरक्त प्रकाश जैसी तरंग दैर्ध्य शामिल हो सकते हैं।
अस्थायी समाधान प्रतिनिधित्व की गई समय सीमा को संदर्भित करते हैं। यह तकनीक समय के साथ परिवर्तन दिखाने के लिए किसी क्षेत्र की अनुक्रमिक छवियों का उपयोग करती है।